
Listen To This Blog
Introduction
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, the ability to analyze and interpret data has become indispensable. Quantitative reasoning stands at the forefront of this shift, offering a powerful toolset for individuals across various sectors. This skillset is not just about crunching numbers; it's about understanding the story they tell and making informed decisions based on that narrative. Whether you're a student grappling with complex mathematical concepts, a professional navigating the intricacies of market trends, or a policymaker aiming to craft data-driven strategies, mastering quantitative reasoning is key to success. In our comprehensive guide, we delve into the essence of quantitative reasoning, exploring its significance, applications, and strategies for effective use. Join us as we unravel the nuances of this critical skill, illuminating how it shapes decision-making processes in diverse fields.
What is Quantitative Reasoning?
Quantitative reasoning is a multifaceted skill that plays a crucial role in our understanding and interpretation of the world around us. It's not just about handling numbers; it's about applying logical thinking to quantify, analyze, and make sense of data. This skill is increasingly vital in a variety of fields, from academic research to business analytics. Let's break down the core aspects of quantitative reasoning:
Data Interpretation and Analysis
- Understanding Numbers: It involves comprehending numerical data, statistics, and figures.
- Analytical Thinking: Applying logic to interpret data and draw conclusions.
Mathematical Applications
- Basic to Advanced Math: Employing mathematical concepts from simple arithmetic to complex algebra.
- Statistical Reasoning: Understanding and using statistical methods to analyze data.
Real-World Applications
- Everyday Decision Making: From budgeting to understanding economic trends.
- Professional Use: In fields like finance, science, technology, and more.
Quantitative reasoning is more than just a set of skills; it's a way of thinking that enables us to navigate the complexities of a data-driven world. It empowers us to make sense of information, foresee trends, and make decisions that are grounded in factual, numerical understanding.
Why Do We Need Quantitative Reasoning?
Quantitative reasoning is more than just a mathematical skill; it's a critical thinking tool that plays a pivotal role in various aspects of our lives. Let's explore why this skill is so essential:
Informed Decision Making
- Data Interpretation: In a world awash with data, quantitative reasoning helps us make sense of numbers, trends, and statistics. It's not just about understanding data, but also about interpreting it correctly to make informed decisions.
- Problem-Solving: Whether in professional scenarios or everyday life, quantitative reasoning equips us with the ability to tackle complex problems by breaking them down into manageable parts.
Enhancing Professional Competence
- Career Advancement: In many fields, from finance to engineering, the ability to analyze and interpret data is crucial. Quantitative reasoning skills can set individuals apart in the job market and open doors to advancement.
- Innovation and Efficiency: Businesses and organizations rely on quantitative reasoning to optimize operations, innovate solutions, and stay competitive.
Academic Excellence
- Educational Foundation: For students, quantitative reasoning is foundational. It's not just for math and science; these skills are essential for subjects like economics, social sciences, and even humanities.
- Critical Analysis: In academics, quantitative reasoning aids in the critical analysis of theories, arguments, and research findings, fostering a deeper understanding of various subjects.
Societal Impact
- Policy Development: Policymakers use quantitative reasoning to evaluate the impact of policies, understand societal trends, and make decisions that affect communities.
- Public Awareness: In an era of misinformation, quantitative reasoning skills help the public critically evaluate the information presented to them, leading to a more informed society.
In summary, quantitative reasoning is a vital skill that enhances our ability to navigate the complexities of the modern world. It empowers us to make better decisions, advance in our careers, excel academically, and contribute positively to society.
Strategies for Effectively Using Quantitative Reasoning
|
Strategy |
Description |
Application |
|---|---|---|
|
1. Problem Identification |
Begin by clearly defining the problem or question at hand. This involves understanding the context and the specific quantitative elements involved. |
Useful in academic research, business analysis, and policy development. |
|
2. Data Collection |
Gather relevant data. This could be through experiments, surveys, or sourcing from existing databases. Ensure the data is reliable and pertinent to the problem. |
Essential in market research, scientific studies, and economic forecasting. |
|
3. Data Analysis |
Employ appropriate mathematical and statistical methods to analyze the collected data. This could involve calculations, statistical tests, or modeling. |
Applied in financial analysis, scientific research, and operational management. |
|
4. Critical Interpretation |
Interpret the results in the context of the problem. Look beyond the numbers to understand what they imply and how they relate to the broader scenario. |
Key in strategic planning, academic thesis work, and policy formulation. |
|
5. Solution Development |
Based on the analysis, develop solutions or conclusions. This involves synthesizing quantitative findings with qualitative insights. |
Useful in business strategy, scientific innovation, and educational methodologies. |
|
6. Communication of Findings |
Effectively communicate the findings and proposed solutions. This includes presenting data in an understandable format, like charts or reports. |
Important in stakeholder presentations, academic publishing, and report writing. |
|
7. Continuous Review and Adaptation |
Regularly review the outcomes and adapt your approach as needed. This ensures the continuous relevance and accuracy of your quantitative reasoning process. |
Applies to ongoing project management, policy revisions, and academic research. |
This table outlines key strategies for effectively utilizing quantitative reasoning across various contexts, ensuring that data-driven decision-making is both accurate and impactful.
Process of Quantitative Reasoning
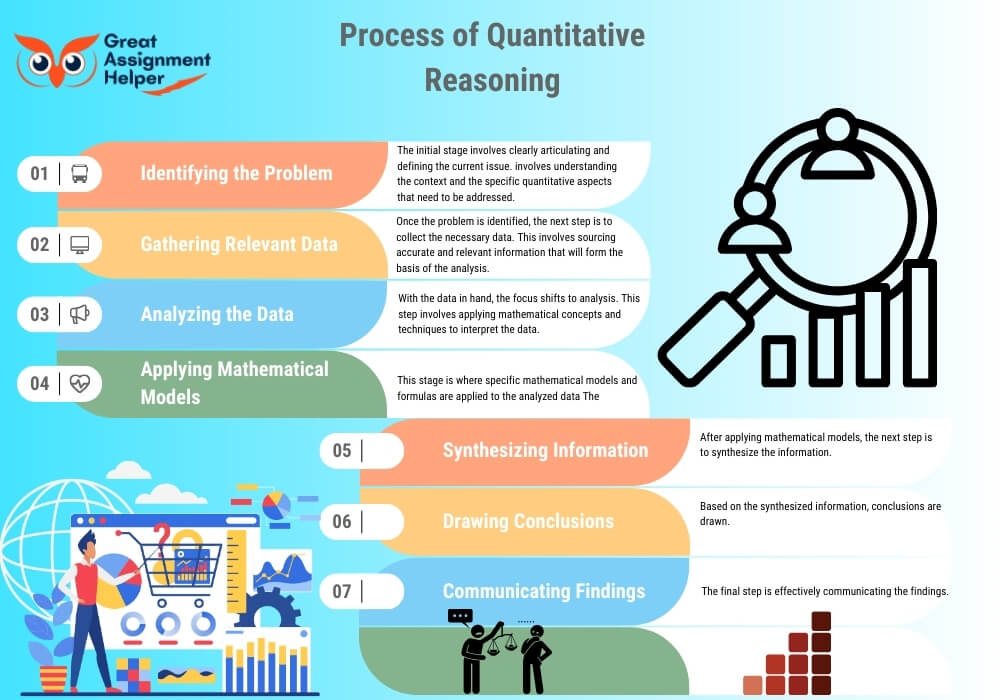
Quantitative reasoning is a multifaceted process that involves several key steps. Each step is crucial in ensuring that the reasoning is accurate, relevant, and applicable to real-world scenarios. Here's a breakdown of this process:
- Identifying the Problem: The initial stage involves clearly articulating and defining the current issue. involves understanding the context and the specific quantitative aspects that need to be addressed. It's about pinpointing the exact numerical or data-driven challenge that requires a solution.
- Gathering Relevant Data: Once the problem is identified, the next step is to collect the necessary data. This involves sourcing accurate and relevant information that will form the basis of the analysis. The quality of the data collected directly impacts the effectiveness of the reasoning process.
- Analyzing the Data: With the data in hand, the focus shifts to analysis. This step involves applying mathematical concepts and techniques to interpret the data. It's about looking beyond the numbers to understand what they represent and how they relate to the problem.
- Applying Mathematical Models: This stage is where specific mathematical models and formulas are applied to the analyzed data The selection of a model relies on the characteristics of the problem at hand and the nature of the data involved.. This step is critical in transforming raw data into meaningful insights.
- Synthesizing Information: After applying mathematical models, the next step is to synthesize the information. This involves combining the insights gained from the analysis to form a coherent understanding of what the data is indicating in relation to the problem.
- Drawing Conclusions: Based on the synthesized information, conclusions are drawn. This is where quantitative reasoning comes full circle, as the data-driven insights are used to make informed decisions or predictions about the problem.
- Communicating Findings: The final step is effectively communicating the findings. This involves presenting the conclusions in a manner that is understandable and useful to those who need to act on this information, whether they are experts in the field or not.
Each of these steps plays a vital role in the quantitative reasoning process, ensuring that decisions and conclusions are not just based on data, but are also logical, rational, and applicable to real-world situations.
Arithmetic: The Foundation of Quantitative Analysis
Core Concepts and Applications
Arithmetic is the bedrock of quantitative reasoning, encompassing fundamental operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. These basic yet powerful tools are pivotal in interpreting and analyzing numerical data across various contexts.
Real-World Relevance
In everyday scenarios, from budgeting in personal finance to calculating measurements in engineering projects, arithmetic serves as a critical component. Its practicality extends to diverse sectors, aiding in accurate decision-making and problem-solving.
Enhancing Analytical Skills
By mastering arithmetic, individuals enhance their analytical capabilities, laying a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical endeavors. This proficiency is not just about handling numbers but also about developing a keen sense of numerical relationships and patterns.
Algebra: The Language of Numbers and Patterns
Algebra, often considered the cornerstone of mathematical understanding, serves as a universal language that deciphers patterns and relationships in numbers. This field is not just about solving equations; it's a journey into the realm of abstract thinking and logical reasoning.
- Equation Mastery: At its core, algebra revolves around the art of balancing equations. It teaches us to find unknown values and understand the symmetry in mathematical expressions.
- Function Analysis: Delving deeper, algebra introduces the concept of functions, a critical tool for mapping and understanding variable relationships.
- Real-World Applications: Beyond the classroom, algebra finds its relevance in various practical scenarios, from calculating financial projections to solving everyday problems.
In essence, algebra equips us with a powerful toolkit for navigating the complexities of both numbers and real-life situations, making it an indispensable part of our intellectual arsenal.
Exploring the World of Geometry
Geometry, an essential branch of mathematics, plays a crucial role in our understanding of the world around us. It's not just about shapes and sizes; it's a language that helps us interpret space and structure.
Key Concepts in Geometry
- Shapes and Their Properties: Delve into the world of polygons, circles, and triangles, understanding their unique characteristics.
- Angles and Their Interactions: Explore how angles define relationships between shapes and contribute to geometric stability.
- Theorems and Proofs: Uncover the logic behind geometric principles, providing a foundation for more complex mathematical reasoning.
Geometry is more than a subject; it's a framework for problem-solving and logical thinking. Whether in architecture, engineering, or everyday life, geometry offers a lens through which we can better understand and interact with our spatial environment.
Ethnomathematics: A Cultural Lens in Mathematical Reasoning
Understanding Ethnomathematics
Ethnomathematics offers a unique perspective by integrating cultural context into mathematical understanding. This approach recognizes that mathematical practices are deeply rooted in the traditions and daily activities of various cultures.
Cultural Relevance in Learning
It emphasizes the importance of cultural relevance in learning, showing how mathematical concepts are not just abstract theories but are intertwined with real-life practices and beliefs.
Diverse Mathematical Practices
This field explores a variety of mathematical practices from different cultures, highlighting how diverse societies approach mathematical problems and solutions in ways that reflect their cultural heritage.
Enhancing Learning Experience
By incorporating ethnomathematics in education, we enrich the learning experience, making mathematics more relatable and engaging for students from diverse backgrounds.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey through the world of quantitative reasoning underscores its pivotal role in various academic and professional arenas. For students grappling with complex mathematical theories, seeking mathematics assignment help can be a game-changer. Similarly, those delving into the intricacies of shapes and spatial understanding can greatly benefit from specialized geometry assignment help. These resources provide tailored assistance, ensuring that learners not only grasp the fundamentals but also apply them effectively in real-world scenarios.
Moreover, the role of assignment helpers cannot be overstated in this context. They serve as crucial guides, simplifying complex concepts and offering step-by-step assistance. For those seeking comprehensive and reliable support, GreatAssignmentHelper emerges as a commendable assignment help service provider. Their expertise in a range of subjects, coupled with a commitment to quality and clarity, makes them an invaluable resource for students aiming to master the art of quantitative reasoning and beyond.

